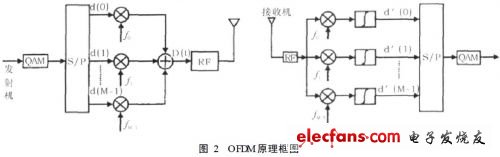
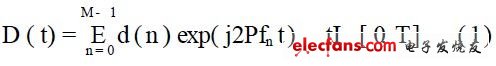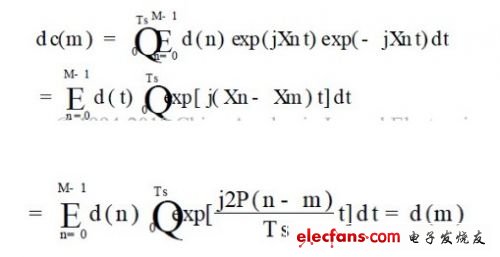1 Introduction In the 21st century, mobile communication technology and the market are developing rapidly. Under the joint action of new technologies and market demands, the third generation mobile communication system -3G has emerged. In 3G, code division multiple access (CDMA) technology is used to deal with multipath problems. To obtain multipath diversity gain. However, in this system, multipath interference and multiuser interference always coexist, and in the case of a large number of users, it is very difficult to implement multiuser detection. And CDMA itself is a self-interference system, all mobile users occupy the same bandwidth and frequency, so in the case of limited system capacity, the more users, the harder it is to achieve a higher communication rate, so the 3G system provides 2Mb/s bandwidth is shared. When multiple users use it at the same time, the average bandwidth that each user can use is much lower than 2Mb/s, and such bandwidth does not meet the needs of mobile users for some multimedia services. The integration and collaboration of technologies in different fields, along with the intelligentization of new wireless broadband technologies and the new services targeted at users, will all breed a new generation of mobile communication systems 4G. Compared to 3G, 4G can provide data transmission rates of up to 100Mb/s, support multimedia services from voice to data, and achieve higher spectrum utilization and lower cost. In order to achieve the above objectives, other breakthrough technologies such as CDMA in 3G must be adopted in 4G, especially to study how to support high data rate data transmission stably, reliably and efficiently under the conditions of mobile environment and limited spectrum resources. . Therefore, OFDM technology is adopted as the core technology in the 4G mobile communication system, which can increase the system capacity, avoid various interferences caused by high speed, and has good anti-noise performance and anti-multipath. Channel interference and high spectrum utilization. This paper introduces the basic principle of OFDM, its modulation/demodulation technology implementation and cyclic prefix technology, and compares OFDM and CDMA technologies in three main aspects. 2 OFDM technology analysis 2.1 Basic Principles of OFDM The basic principle of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing can be summarized as follows: a high-speed data stream is transmitted through serial-to-parallel conversion and distributed to several sub-channels with relatively low transmission rates for transmission. In the frequency domain, the channel is divided into a plurality of mutually orthogonal subchannels, each of which has its own carrier modulated separately, and the signals are independently transmitted through the respective subchannels. Since the multipath propagation effect causes the received signals to overlap each other, mutual interference between the signal waveforms is generated, and inter-symbol interference is formed. If the bandwidth of each subchannel is sufficiently narrow, the frequency characteristic of each subchannel can be approximated as flat. of. As shown in Figure 1. Therefore, each subchannel can be regarded as an ideal channel for inter-symbol interference. In this way, the received signal can be reliably demodulated without using complex channel equalization techniques at the receiving end. In an OFDM system, orthogonality between frequency domain subchannels is ensured by inserting guard intervals between OFDM symbols, and interference between OFDM symbols due to multipath propagation effects is eliminated. Therefore, OFDM is particularly suitable for transmitting data at high speed in a mobile radio channel in which multipath fading is present. The principle block diagram of OFDM is shown in 2. As shown in FIG. 2, the original high-rate bit stream is converted into a plurality of sets of low-rate bit streams d(M) after serial/parallel conversion, and these d(M) are modulated to become corresponding frequency domain signals, and then pass through. The cyclic prefix and the D/A transform are added and transmitted through the RF; after being propagated through the wireless channel, the receiver receives and demodulates in the reverse order of the transmitter, thereby obtaining the original transmitted signal. In Figure 2, d(M) is the Mth modulation symbol; the expression of the OFDM modulated signal D(t) in the figure is: In the formula (1): T is the symbol period plus the guard time; fn is the frequency of each subcarrier, which can be expressed as: In equation (2): f0 is the lowest subcarrier frequency; Ts is the symbol period. At the transmitting end, the transmitted data is modulated by conventional QAM to form a baseband signal. Then, it is serially transformed into M sub-signals, which then modulate M sub-carriers that are orthogonal to each other, where /orthogonal 0 represents an accurate mathematical relationship between carrier frequencies, and its mathematical expression is QT0fx(t)fy(t ) dt = 0, and finally added to the OFDM transmission signal. The actual output signal can be expressed as: At the receiving end, the input signal is divided into M branches, which are mixed and integrated with M subcarriers respectively to recover the sub-signals, and then the data can be recovered by parallel-serial conversion and conventional QAM demodulation. Due to the orthogonality of the subcarriers, the mixing and integrating circuits can effectively separate the subcarrier channels as shown in the following equation: Where dc(m) is the mth branch sub-signal at the receiving end. The main difference between OFDM and other technologies in the whole OFDM workflow is the modulation/demodulation technology and the addition of cyclic prefix. The following is a detailed analysis.
Water-Cooled Capacitor is supercapacitor is a capacitor with a capacity of thousands of farads.According to the principle of capacitor, capacitance depends on the distance between the electrode and electrode surface area, in order to get such a large capacitance, as far as possible to narrow the distance between the super capacitor electrode, electrode surface area increased, therefore, through the theory of electric double layer and porous activated carbon electrode.
Water-Cooled Capacitor,Water-Cooled Power Capacitor,Water-Cooled Electric Heat Capacitor,Water-Cooled Electric Heating Capacitor YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD , https://www.yzpstcc.com