In recent years, information technology has become more and more widely used in automobiles, including the introduction of various software. Some cars are equipped with an electronic control unit (ECU: Electronic Control Unit) of more than 100. The program code is said to be up to about 10 million lines, and the car has become a system with a large amount of software.
Cars that have become a collection of software are now facing new threats (Figure 1). In 2010, researchers in the United States found that through the communication channels inside and outside the car, the vulnerability of the vehicle software could be attacked, thus affecting the vehicle's control system. This shows that although the on-board system and the information system that focus on real-time are different, in-vehicle software has weaknesses in information security in terms of authentication and communication confidentiality.
Moreover, the possibility of attack on the in-vehicle software system will increase in the future. This is because the path of attack is increasing. There are more and more types of external interfaces of the vehicle. In addition to the fault diagnosis function "OBD-II" and the charging control interface, it also includes functions linked to smartphones and tablets.
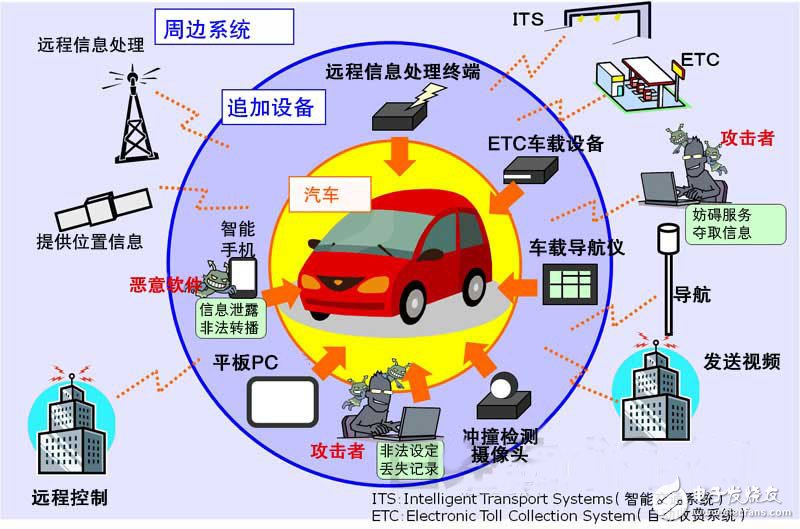
Figure 1: Car-related systems and threats
This article will introduce why the car needs information security, the car threat and countermeasure analysis conducted by the Japan Information Processing Promotion Agency (IPA), and information security enhancement measures.
Why do cars need information security?
It is not new to adopt information technology such as control software in automobiles. As early as 1980, software with about 2000 lines of code was embedded in the ECU. So why is the car starting to need information security today?
This is not only because the software mentioned in the opening section has expanded thousands of times, but also related to the three major trends in automotive technology.
The first trend is that with smartphones as the center, the link between cars and the Internet is becoming more and more common. One big difference between smartphones and traditional phones is that customers can develop applications and offer them to anyone more freely. From simple applications to practical types, there are a wide variety of applications in the market. Automotive-oriented applications have also emerged.
The problem is that some of these applications are poorly reliable. Hackers may use the vulnerability to use smartphones as a springboard, causing damage to in-vehicle devices and car navigation systems, or leaking in-vehicle information via smartphones, infringing the privacy of drivers. Moreover, using a smartphone means that the car is connected to the external network at any time. Therefore, it is possible to attack an automobile that is traveling via an external network and a smartphone.
In addition to smartphones, functions such as ETC (automatic toll collection system), smart car keys, and the like are connected wirelessly and externally, and the function of connecting an electric vehicle (EV) to an in-vehicle network via a charging plug is also becoming widespread.
In the future, as cars begin to connect to the off-board network anytime and anywhere, it is exaggerated to say that attackers can attack cars around the world across the network without having to get close to the car. Even if you don't access the network anytime and anywhere, the maliciously downloaded smartphone from the user may be harmful to the car.
Wide range of general-purpose systems for in-vehicle equipment
The second trend is that the impact of in-vehicle software and in-vehicle LAN on the basic control functions of the car's “driving, turning, parking†is increasing. For example, car manufacturers use communication or information terminals to provide door lock control, adjust engine power, and update software. Once these functions are successfully invaded by hackers, they are likely to cause major harm.
Moreover, in order to reduce the cost while ensuring versatility, some in-vehicle systems have begun to use a general-purpose operating system such as Linux. It is more and more convenient for car users to use various services, but the difficulty of parsing and attacking the operating system is also getting lower and lower.
Not only the operating system, but also the versatility of the in-vehicle LAN. For example, the German government-assisted project "SEIS (Security Embedded IP-based System)", the project is considering the use of "Ethernet" for the in-vehicle LAN and the standard communication protocol "TCP/IP". In 2008, BMW used Ethernet as one of the in-vehicle diagnostic interfaces to rewrite software.
In the past, the "CAN (Controller Area Network)" as a representative, the communication method of the in-vehicle LAN has been standardized at the circuit level, but the specific contents of the request command and response mechanism are mostly different from the enterprise, and constitute the actual application. "obstacle". But from the perspective of information security, such "obstacle" is actually a "firewall."
However, nowadays, adapters for providing in-vehicle LAN communication content using networks such as short-range wireless communication "Bluetooth" and WLAN have appeared on the market. As more and more in-vehicle LANs adopt Internet standards, numerous devices and information systems inside and outside the car will be closely connected to the car. Connecting a car LAN is becoming easier and easier, and breaking through the "firewall" becomes a breeze.
Time when I am not waiting
The third trend is that with the adoption of EV and ITS (Highway Traffic System) technology, the need to exchange vehicle information with the outside world is increasing. EVs use information processing technology to manage large-capacity batteries, and their functions are to manage the state of charge, the number of charge and discharge cycles, and the like of extremely expensive batteries.
One of the specific cases is not to save the charging situation inside the EV, but to record it to the system of the network server. The system collects data such as the number of times of charge and discharge of the battery and the amount of charge, and stores it on the server. Communication uses PHS and 3G/4G mobile phones. In addition, the United States is also studying how to use EV's state of charge management information to achieve services such as car sharing.
In addition, compared with gasoline vehicles, EVs have a more abundant environment, and the space for handling in-vehicle systems that handle information will be larger.
Services that make full use of vehicle information through the use of ITS technology are also being explored. Previously, it was confirmed that the road conditions depended on the cameras installed on the roads. In the future, by sharing the information of each vehicle, the driver is expected to have more detailed and accurate road conditions. To achieve this, car access to the Internet is a necessary condition. Moreover, in order to promote services, the voice of the development and disclosure of communication protocol standards is expected to rise.
In addition, in the future, if ITS technology is applied to functions such as autonomous driving, it is becoming more and more important to ensure information security in order to realize a car society that can control automobiles such as automobiles through external information.
From the attacker's point of view, the three major trends described above are like constantly creating convenience for car hackers. Access to the external network will undoubtedly create an entry for the attack; if the universal system is popular, the difficulty of the attack will be reduced; the diversification of services means that the car has a large amount of information, as long as the valuable information is stolen, it can directly profit.
Of course, as long as you can hijack the car key and the engine starting system, stealing the car is also a breeze. Moreover, the impact of hijacking cars is not limited to individuals, and the transportation facilities in which numerous cars pass through are one of the foundations of society. In the United States and Europe, which are vigorously fighting terrorism, research on government-led automotive information security measures is advancing. Even from the perspective of a stable society, taking safety measures for automobiles will become a must-do in the future. For companies involved in car development, the relevant measures to study car safety can be said to have been waiting for us.
1,2.4G Digital Wireless Backup Camera System for Truck/Van/Caravan/Trailers/Camper/Pickup/5th Wheel/Bus. Easy to install, no more complex wiring.
2, 7-Inch TFT LCD screen Monitor with Built-in Wireless Receiver-- High resolution image and full color display.
3,Rearview IR Reverse HD backup Camera with Built-in Wireless Transmitter---with 12/18/28 individual Infrared (IR) LED for Night Vision. Hard Metal Cased Camera with IP68 Waterproof and Mud proof, Designed and tested for extreme climates.
4, Voltage Range From 12-32V DC Power, Flexible Vehicle Compatibility.
5, Digital wireless technology for specialty vehicles , No any interference with other wireless devices, if you ensure stable and high resolution image with 100M acceptance range in open areas.
Wireless Backup Camera For Car,2.4G Wireless Backup Camera System,Wireless Backup Camera Kit,Wireless Led Backup Camera Kit
Shenzhen Sunveytech Co.,LTD , https://www.sunveytech.com