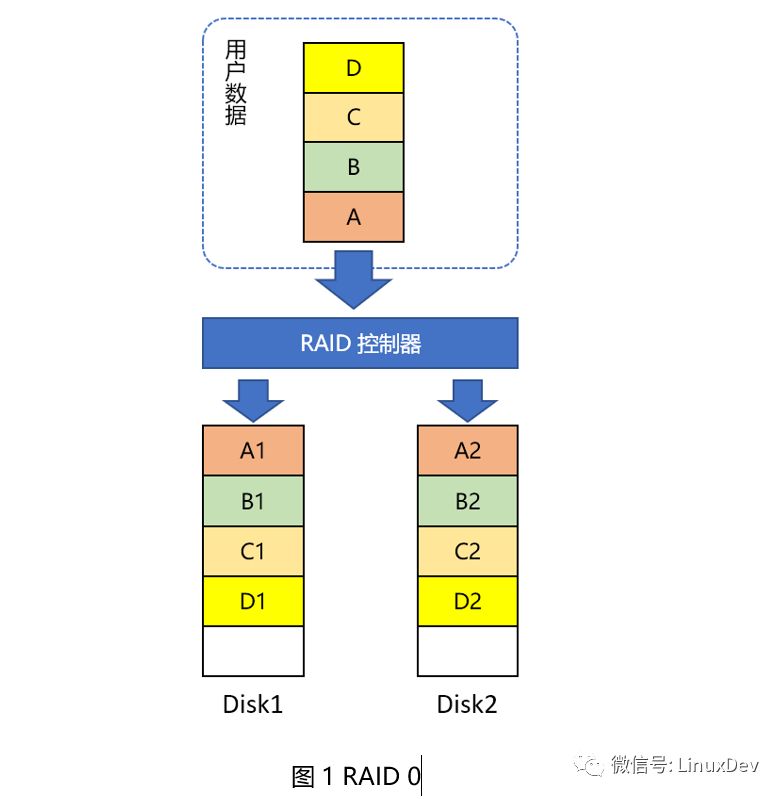
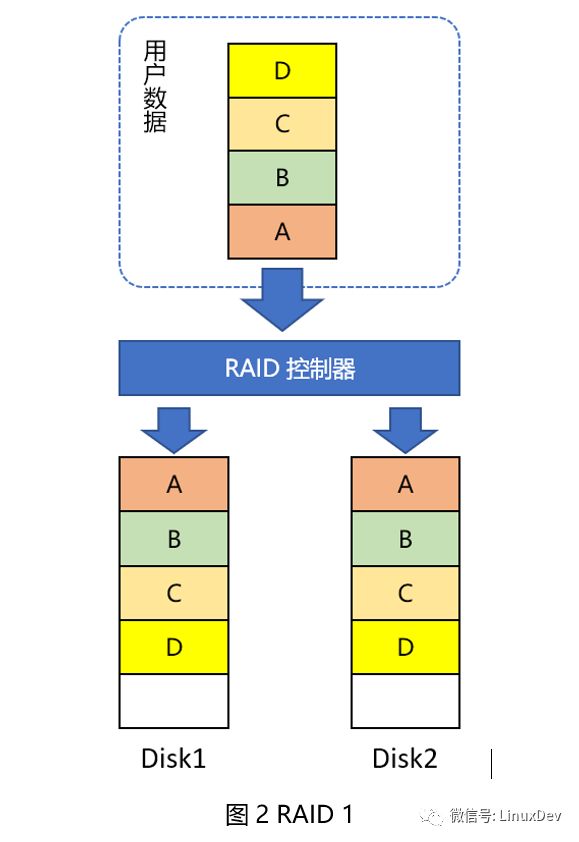
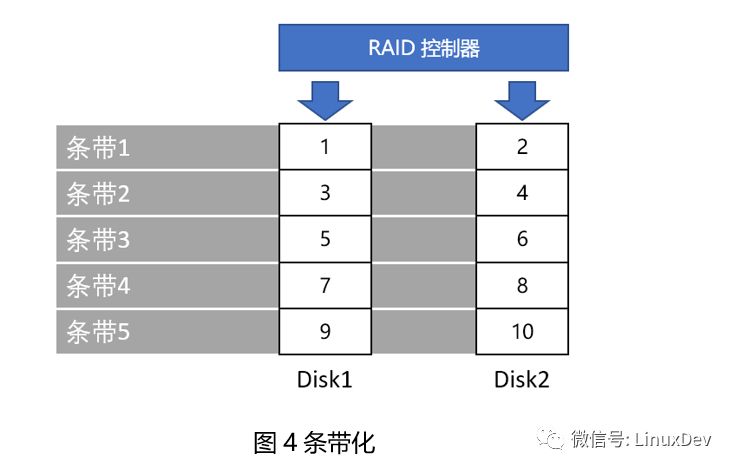
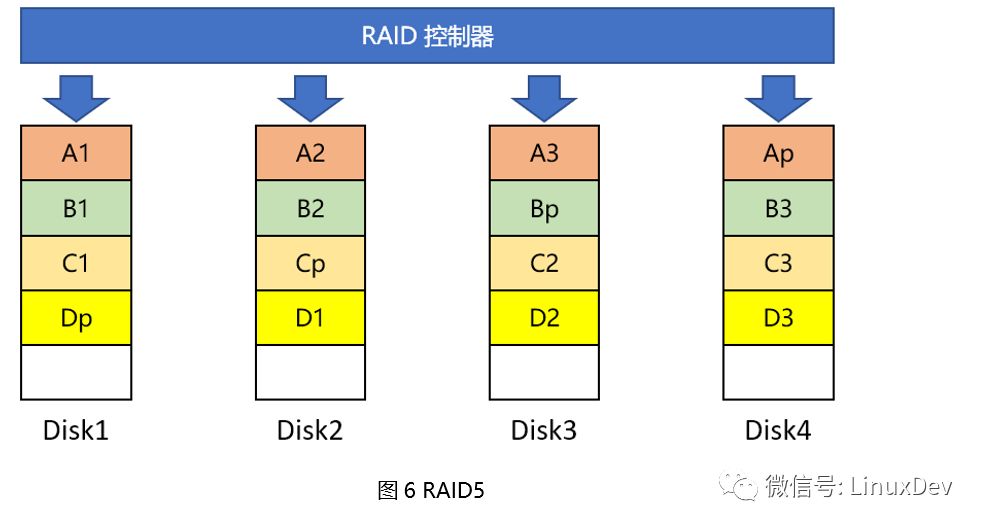
Primers helping people makes a person happy. This era needs sharing, interaction, and collisions to make progress. The theme that I want to share today is "What about storage devices?" What are the keywords that need to be highlighted in this sentence? Is "storage"? Is "device"? No, it is "that." As a primary school student who has just entered the storage industry for less than two years, the limited ability level is in general, relying on the pressure of mortgage loans to come to this day. Storage involves all aspects and is limited by its capabilities and space. The main purpose of this article is to make everyone aware of the storage aspects of some emotional, there is no in-depth technical details. Readers will surely have industry predecessors, technology leaders, open source community masters, and chiefs of African tribes, all of which are inseparable. There are also deficiencies and criticisms. Speaking of storage devices, some of you may think of these: tapes, floppy disks, hard drives, USB flash drives, and CDs sold by early street middle-aged women (have you bought them? With the development of the Internet, this industry has declined, !). The storage devices we are going to talk about today are slightly more advanced than these, but in the end they have not broken away from them. I have a 1TB mobile hard disk, which is almost full, and I have some concerns recently. In case I accidentally fall to the ground, I will be scrapped. The information and memories accumulated over the years will be lost. I have to think of a solution. Who said that there is no cloud disk? Frankly speaking, I don't trust cloud providers. I don't just condemn the technical level of distrust, who cares if they are not. Someone else gave advice to the entire RAID. Yes, we start with RAID. What is RAID? The foreign language description of RAID is Redundant Array of Independent Disks. The Mandarin language is usually translated into: redundant array of independent disks. Playing brothers and sisters, playing father and son soldiers, a hard disk may be a variety of problems, RAID is a group of hard drives through a variety of combinations, showing a logical hard drive, make up for some of the individual hard disk defects (such as IO performance, data protection), this The logical hard disk is almost the same as a single hard disk from the perspective of the user and is transparent to the user. Summarized one sentence: Basic friend walks together in his life, single person's pain no longer has. RAID level The RAID level is a combination of hard disk types, such as: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 01, RAID 3, RAID 5, RAID 6, and so on. Many, comic actor can write a consistent performance, This time, I will pick a few common ones. RAID0 The simplest RAID0 consists of two hard disks. As shown in Figure 1, when a user writes data, for example, data block A, it actually divides several blocks A into two parts and writes them to Disk1 and Disk2 respectively. , C, D are the same operations. As you can see, RAID0 does not solve the problem I encountered earlier. Any disk on Disk1 or Disk2 is broken, and the saved data is lost and the data is not protected. Of course, the advantages are obvious. Data is written into two disks in parallel, which takes less time, theoretically saves 50% of the time, and has good IO performance. We can also use more disks to make up RAID 0. In that case, the data blocks will be divided into more points. Writing to multiple disks in parallel will take less time. The status of the various hard drives that make up RAID0 is equal. There are task brothers sharing the roles. No one's role is special. RAID1 You have everything I have, wow, and you're like, that's RAID 1, don't believe it, just look down. As long as two hard drives can form a RAID1, as shown in Figure 2. The characteristic of RAID1 is that the data blocks written by the user are written to each hard disk that forms RAID1 at the same time. The data saved by these hard disks is exactly the same. So, one of the hard drives is damaged, don't be afraid, another hard drive still saves the complete data. Someone wanted to ask, "What if the two hard drives are broken?" Friends, are we chatting? In essence, RAID1 is doing backups. We do not often copy files from a computer to a USB flash drive or a mobile hard disk for backup. Only this backup is real-time, and the user backs up each time he writes a piece of data. Adding more hard drives to form RAID1 also increases the number of backups and is more secure, but it takes more money to buy hard drives. Of course, local tyrants such as Acong also said. RAID3 Before you say RAID3, you're going back to a few words. In the illustrations of the previous RAID0 and RAID1, each hard disk draws some small cells and stores A, B, or A1, A2, and so on. Dividing these small grids is called striping and is a new term. There is no way to get a name for new things. In the early years, people in management forums were called moderators, and those who maintained blogs were called bloggers. Now, the person who establishes the WeChat group is called the owner of the group and establishes and maintains the public number. princess? Did Song agree? Feel the effect of disk striping. As shown in Figure 3, the two disks are not striped. User data comes over to write Disk1 first. After Disk1 is written, Disk2 is written. How do you feel about this RAID? It neither improves IO performance nor protects data, and then sounds like a RAID. Whoever sells this RAID, as a qualified person, can't burst into foul language and call him on behalf of him for 100 dollars. Someone asked (Yes, that person who asked the question earlier): "This example is too extreme. If I have a large file, I can calculate that 6 to 10 parts will eventually be saved to Disk2, then I can parallelize Write 1~5 to Disk1, 6~10 to Disk2â€. If Disk1 is a 1TB hard disk, how big is your file? More than 1TB, how many scenes in the real world exist such a large file? We continue. Figure 4 shows the disk format after striping. If no striping is stored on a disk, a disk is full and another disk is written. Then after striping, it is stored in units of strips. Write a strip and write a strip. The same area (offset position and size determination area) of each disk of RAID constitutes a stripe. Then look at RAID3, as shown in Figure 5. Disk4 is unique, as a checksum, it does not save user data, but saves the user data checksum. Ap is an XOR operation check value of A1, A2, and A3. Similarly, similar to Bp~Dp. The advantage of this is that if one of the 4 disks has a broken disk, we can read the data from the other 3 disks and perform an exclusive OR operation again to calculate the data of the damaged disk. This process is called data reconstruction. Take a chestnut: Assuming that the initial A1=1, A2=0, A3=1, calculate Ap=A1^A2^A2=1^0^1=0 when saving. Now Disk3 is corrupted, we have to calculate A3, A3=A1^A2^Ap=1^0^0=1. Got the correct A3! Consider the characteristics of RAID3, one of which can be written in parallel. Second, there is a verification disk that allows a disk failure. Third, in particular, if the check disk is damaged, it will not affect the user's read operation at this time. There are also disadvantages, that is, when the user writes data, no matter which data disk to write data, you need to rewrite the check-up disk at the same time. For frequent applications of the write operation, the load of the check-up disk is very large and becomes a bottleneck. . So, can we balance the time-consuming and laborious work of checking data? Can't be old enough to be alone. RAID5 RAID5 does not have a separate parity disk. Find the position of Ap, Bp, Cp, and Dp from the image below. What did you find? Right, each disk acts as a data disk and a parity disk. The checksum is written to this load and distributed to each disk. The check disk bottleneck encountered by RAID3 in front does not exist. When a disk fails, RAID cannot continue to provide services. In general, the operation and maintenance personnel replace the failed disk. After the new disk is in place, RAID rebuilds the data and uses the check algorithm to restore the lost data to a new disk. , and then RAID can continue to provide services. Some systems support hot spare disks. When a disk (disk 2) in a RAID fails, the system selects a disk (disk 5) from the hot spare disk to replace the role of the failed disk. Then RAID immediately rebuilds the data, thus minimizing the number of disks. The time when RAID stopped the service. That's right, the hot spare is the spare tire. RAID5 can improve performance in parallel IO, data verification plays a role in data protection, and there is no bottleneck in the checkup disk. It looks good. Someone asked (Yes, still the person who asked the question earlier): "What if there are 2 disk failures at the same time?" "Then use RAID6, you can tolerate 2 disk failures." "What if you have 3 disk failures at the same time?" Hey, what is the company? I will add another 100 yuan and I will come to personally. Yes, we must set the egg. Although RAID has a lot of advantages over a single hard disk, it is not the best, there are problems that cannot be solved, and there are extreme situations in which Hold cannot live. RAID6 and other RAID forms no longer develop. You can visit here to continue further studies: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_RAID_levels By the way, RAID 2.0 emerged later in the development of RAID, a technology that does not consist of a single disk as a basic unit of RAID. Two flowers bloom, each one. Said so much about RAID content, for end users? How to use RAID? This is a problem. Of course, users can buy a few hard drives to form a RAID. When they are used as "big hard drives", they can be tolerated for desktops, and the chassis can be easily installed. So what about laptop users? No place to install ah. USB external? You walked into Starbucks elegantly, asked for a cup of coffee, took out the tall Apple computer, and piled up a hard disk on the side of the table. You told others not to touch, saying that it was your RAID? Is this leisure or a stall? In this world, as long as there is demand, even if the abnormal needs, there will be businesses to meet you. I want to keep fit, and some businesses will mix Chinese medicine and wine, come on, wine, can make up for it.
The Privacy Screen Protector can display a black screen directly in front of the screen at an angle greater than 30° to effectively block the sight of people next to it, while achieving a perfect balance between black screen privacy and daytime clarity.
The Screen Protector can protect the edges and gaps of the display so that it can extend to the entire screen surface, thereby achieving maximum coverage without any exposed space.
The Self-Healing Screen Protector can provide the best protection for your phone from drops, bumps, scratches and normal wear and tear. Using an oleophobic waterproof coating can prevent sweat and grease from remaining on your fingerprints, keeping you simple all day long.
The 0.14mm thick Ultra-Thin Protective Film has a "real touch" feel and ensures fast response performance.
If you want to know more about Privacy Screen Protector products, please click the product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Privacy Screen Protector.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about the Privacy Screen Protector!
Anti-peep Screen Protector, Privacy Screen Protector, Anti-spy Screen Protector, Privacy Protective Film, Privacy Hydrogel Film,Anti-peeping Screen Protector Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjthydrogelprotector.com