introduction With the rapid development and widespread popularity of information technology and computer network technology, more and more families are getting information and information through the Internet or intranet. As a modern intelligent residential community, providing broadband multimedia integrated information and information services to the majority of residents in the community is an important manifestation of intelligent housing and an objective need for the development of the information society. The Housing Industry Office of the Ministry of Construction put forward the concept of residential intelligentization in China, that is, the intelligentization of residential communities is to realize the intelligent control of remote homes by using 4C (computer, communication, network, automatic control, IC card) technology, through an effective transmission network, The integration of telematics service and management, property management and security, and residential intelligent system provides high-tech intelligent means for the service and management of residential communities, in order to achieve fast and efficient value-added service management and provide a safe and comfortable home environment. 1 System Introduction The development of home intelligent control systems is based on short message technology, automatic control technology, computer technology, digital communication technology and encryption technology. The system utilizes related networks, computer systems and controllers, and uses wireless networks and wired networks as basic control commands and data information transmission methods to realize wireless remote control and data transmission of mobile phones. Provide a full range of digital services for home and community management through a dedicated SMS control center and service center. The home intelligent control system has the functions of mobile phone remote control, automatic alarm, call community service, property management, etc. It can also be expanded infinitely according to the needs of the user group to the living network service and smart office. The device is connected to the Internet/Intranet network. In principle, as long as the TCP/IP network protocol is implemented. The TCP/IP protocol and its applications are a complex system engineering. The establishment of the agreement has undergone a rigorous design process, and the implementation of the full set of protocols is more complicated. In an embedded system, implementing the protocol has certain difficulties. In practical applications, if the protocol is to be fully implemented, a more reasonable solution is to directly use the integrated TCP/lP protocol chip to separate the central control unit and the TCP/IP protocol processing unit. On the other hand, in other implementations, the original TCP/IP can be simplified, and some protocols required by the actual application system are retained, so that the core chip can realize the data transmission of the network and complete the monitoring task. Streamlining the original TCP/IP protocol can greatly reduce the difficulty of system implementation and improve the efficiency and reliability of the system. The block diagram of the system is shown in Figure 1. The three-level power in the family is used as the acquisition signal, and is processed by the sample-and-hold circuit, and then sent to the single-chip microcomputer for processing. The MCU sends the data to the E5122 network protocol processor through the serial port for packet processing, and packs the data into a TCP/IP protocol packet, which is sent to the Ethernet through the RTL8019AS Ethernet controller. The CPLD chip EPM7128S is used as the decoding and driving circuit. In this application, the rate of data exchange by the home user terminal is not high, and is below 1 MB/s. Therefore, a general high-speed single-chip microcomputer can be used to write the TCP/IP protocol, which can satisfy the requirements and the price can be accepted by the user. 3 chip introduction (1) Network Interface Controller RTL8019AS RTL8019AS is Realtek's highly integrated dedicated Ethernet interface chip, supporting EtherneTII, IEEE802.3, 10Base5, 10Base2, 10BaseT, supporting UTP, AUI & BNC, PnP automatic detection mode, and embedded 16KB SRAM for transceiver buffer, reducing the pair The speed requirement of the main processor. Supports 8-bit, 16-bit data bus mode; supports jumper and no jumper mode; has full-duplex communication interface, which can send and receive data simultaneously on the twisted pair through the switch, increasing the bandwidth from 10M to 20M. The ideal chip for Ethernet communication. The RTL8019AS has three working modes: 1 Jumper mode, the I/O and interrupt of the network card are determined by the jumper; 2 Plug and play mode, automatic configuration plug and play by software; 3 Jump-free mode, the I/O and interrupt of the network card are determined by the contents of the external 93C46. Which method the NIC uses is determined by the 65th foot JP of the RTL8019AS. When the 65-pin JP is high (connected to VCC or pulled through a 10kΩ resistor), the jumper mode is used; when the RTL8019AS pin is left floating, the input state is low (other pins are also the same, the floating input pin level) Low level, there is a 100kΩ pull-down resistor). (2) TCP/IP protocol parsing chip E5122 E5122 is a Feihong series network protocol processor developed by Shanghai Fine Technology Co., Ltd. The external crystal oscillator is 22.1184MHz and the operating voltage is 5V. The hardware implements the TCP/IP protocol and provides an API interface, which greatly facilitates the use of externally integrated RAM. The user terminal communicates by I2C protocol or RS-232 interface mode, the communication interface supports the MPU with I2C interface, and the I2C driver is provided for the MPU without the I2C interface. The interface between the E5122 and the network is an Ethernet interface, which is connected to the Ethernet through the Ethernet control chip RTL8019. The serial rate is up to 115.2Kbps for true real-time delivery. The E5122 is a dedicated chip that implements the TCP/IP protocol to implement protocol conversion between Ethernet and serial ports. It can provide a complete network communication solution for serial devices, and only needs an external MPU. The MPU model used in this system is: 89C52 single chip microcomputer. In the MCU program, you only need to simply call the API function to achieve it. The structure of E5122 is shown in Figure 2. When the device is connected to the network, the client actively requests to connect to the server as a passive device, and receives the connected intranet to receive the remote query access of the remote client, and returns the device information to the client. Similarly, it can also act as a client to communicate with hosts on the LAN or on the Internet. The E5122 uses 32KB of RAM externally and is used as an Ethernet data buffer to store system parameters using a 256-byte (minimum 256-byte) serial EEPROM (I2C bus interface). The user communicates with the E5122 through the serial port. E5122 Completes the TCP/IP protocol and serial communication protocol. Supports common serial port and user equipment to interact with each other, and realizes network connection through an external RTL8019AS Ethernet control chip. When the system is running for the first time, the E5122 will initialize the RTL8019AS and set its working mode and interrupt source. The E5122 interrupt is triggered when the RTL8019AS receives data. At this time, E5122 selects the register address and memory address of RTL8019AS through A8~A13 and A15, and controls and realizes data reading. When data is sent to the RTL8019AS via E5122, the RTL8019AS corresponding register is set by the address line for data transmission. 4 hardware circuit design In the specific use, due to the limitations of the microcontroller itself, a series of simplified designs have been carried out. The jumper works by way, the JP pin is connected to the high level; the E5122 and RTL8019AS interface are used to transmit network data. When the system is running for the first time, the E5122 will initialize the RTL8019AS, set the working mode of the RTL8019AS, and set the interrupt source. When the RTL8019AS receives data, it will trigger the E5122 interrupt. At this time, E5122 selects the register address and memory address of the RTL8019AS through A8~A13 and A15 to control and realize data reading. When data is sent to the RTL8019AS via E5122, the corresponding register of the RTL8019AS is set by the address line for data transmission. The interface circuit diagram is shown in Figure 3. In the actual application process of the system, pay attention to the following issues. (1) Transmission speed In the system, the speed of data exchange between the upper PC and the lower measurement and control device depends on the transmission speed of the Ethernet interface module. The transmission speed of the Ethernet module depends on the speed of the Ethernet interface chip, the processing speed of the microcontroller, and the way the device exchanges data. In the general measurement and control system, only the control commands and measurement data are transmitted, and the amount of data is not large. The module and the measurement and control equipment are connected by serial ports such as RS-232, RS-485, CAN, etc., and the communication rate is only several tens of kb/s or hundreds of kb/s. At this time, the speed of the Ethernet interface chip (10Mb/s) and the speed of the microprocessor are much greater than the serial communication speed. Therefore, the transmission rate mainly depends on the communication speed of the serial port. When the data rate to be transmitted is very high (such as an image), it can no longer use a serial port connection with the measurement and control device, but must use a parallel port connection, and the transmission rate depends on the processing speed of the microprocessor. At this time, you should use some high-speed single-chip microcomputers, such as P89C52RX series or SX series. (2) IP address In the Ethernet measurement and control system, the measurement and control device enters the Ethernet through the module, and must determine its own IP address. There are two ways to obtain an IP address: a dynamically obtained IP address and a fixed assigned IP address. Since the E5122 does not support the RARP reverse address resolution protocol, it cannot obtain a dynamic IP address and can only use a fixed IP address. (3) Security control In the small closed LAN, measurement and control, security issues are not big, but in the WAN or even the Internet for measurement and control, security control is crucial. To this end, 48~128 user passwords are used to protect the security of the measurement and control equipment. A legitimate user can modify and set his or her own password. An illegal network user cannot operate the device even if he or she steals the IP address and does not have a user password. (4) Real-time problems The measurement and control system emphasizes its real-time performance in many occasions, but Ethernet is not a real-time system. Because of its carrier sense collision detection (CSMA/CD) communication mode, it determines that the transmission of IP packets in Ethernet will have delay or even packet loss. This is the biggest disadvantage of using Ethernet to form a distributed measurement and control system. However, the speed of Ethernet is getting faster and faster, hundreds of megabytes or even gigabit networks, or in some small closed LANs, the busyness of the network is greatly reduced, the IP packets have almost no collision, and the transmission delay and packet loss phenomenon It is greatly reduced and will not affect the normal operation of the measurement and control system. At the same time, on the network layer of the system, the response protocol can be increased, and the problem of packet loss can be basically overcome. (5) Connection method The module has two sockets: one is an RJ-45 socket, which can be directly connected to the Ethernet with a twisted pair; the other is a 25-pin socket with an RS-232 or RS-485 bus interface. Conclusion With the advent of the 21st century, human beings have gradually entered the information age. With the advancement of technology and the continuous improvement of the quality of life requirements, people's choice and use of home appliances has shifted from focusing on the single function of home appliances to the convenience of purchasing home appliances and control. The development of information technology and network technology has made it possible to centrally control and remotely control the home environment of home appliances. Integrating information technology with home appliance control technology to achieve greater informationization and automation of family life, satisfying people's comfortable and high-tempo life needs, and making all consumer electronic products have the ability to connect to the network. The next step in the development of consumer electronics. The networking of home appliances will bring new demands to the already saturated home appliance consumer market. Further research in this area has brought about tremendous changes in people's lifestyles, working methods and ways of thinking. It has also stimulated the growing demand for various data sources and network services, injecting new life into the information society. And vitality, with important theoretical, practical and commercial value.
figure 1
2 system working principle  64-pin AUI, this pin determines whether to use AUI or BNC interface. The NIC interface we use is generally BNC, and AUI is rarely used. The BNC interface supports 8-wire twisted pair or coaxial cable. Use AUI interface when high level, float low, use BNC interface. The IOCS16B pin is pulled low with a resistor, and the 8-bit data bus mode is selected. The BROM module is omitted, and only 8 data lines SD0~SD7 are needed. The base address selection pins IOS3, IOS2, IOS1, and IOS0 are connected to a low level. Because the pull-down resistor is connected inside the chip, the I/O base address is 300H, so the address lines SA8 and SA9 are connected to the high level. Also, since the address offset of the register is 32 from 00H to 1FH, only the address lines SA0 to SA4 are used, and the remaining address lines are grounded. The interrupt line of the chip is determined by IRQS2, IRQS1, and IRQS0. When all are connected, the interrupt line is INT0, and the 8 interrupt lines are empty. When the SMEMRB and SMEMWB pins determine the network interface type, 10BaseT, 10Base2, or 10Base5 is low when floating mode is used. This is the automatic selection method. The AUI pin determines whether to use the AUI or BNC interface, which is low when floating. The BNC interface is used to support twisted pair or coaxial cable. The pins used are: TPIN+, TPIN-, TPOUT+, TPOUT-. The access network card is coupled to the isolation transformer, and the RJ45 plug is used to connect to the network.
64-pin AUI, this pin determines whether to use AUI or BNC interface. The NIC interface we use is generally BNC, and AUI is rarely used. The BNC interface supports 8-wire twisted pair or coaxial cable. Use AUI interface when high level, float low, use BNC interface. The IOCS16B pin is pulled low with a resistor, and the 8-bit data bus mode is selected. The BROM module is omitted, and only 8 data lines SD0~SD7 are needed. The base address selection pins IOS3, IOS2, IOS1, and IOS0 are connected to a low level. Because the pull-down resistor is connected inside the chip, the I/O base address is 300H, so the address lines SA8 and SA9 are connected to the high level. Also, since the address offset of the register is 32 from 00H to 1FH, only the address lines SA0 to SA4 are used, and the remaining address lines are grounded. The interrupt line of the chip is determined by IRQS2, IRQS1, and IRQS0. When all are connected, the interrupt line is INT0, and the 8 interrupt lines are empty. When the SMEMRB and SMEMWB pins determine the network interface type, 10BaseT, 10Base2, or 10Base5 is low when floating mode is used. This is the automatic selection method. The AUI pin determines whether to use the AUI or BNC interface, which is low when floating. The BNC interface is used to support twisted pair or coaxial cable. The pins used are: TPIN+, TPIN-, TPOUT+, TPOUT-. The access network card is coupled to the isolation transformer, and the RJ45 plug is used to connect to the network. 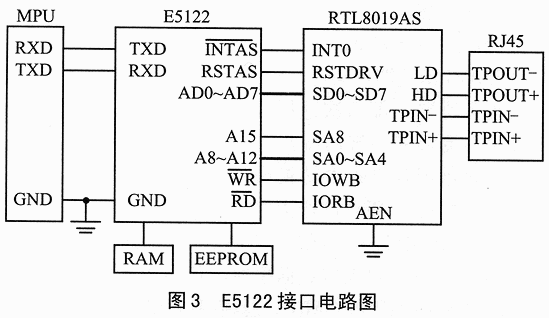
5 Several technical issues in the application